Question:
How is my tax bill calculated?
Answer:
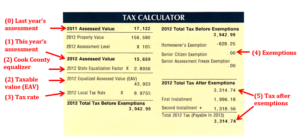
Your tax bill is based on your current assessment, current equalizer, current tax rates and any exemptions you are entitled to as a homeowner.
Here’s how the bill is computed:
- Your tax bill reflects the current assessment of your property. If an appeal was filed– and if you won that appeal – the reduced assessment will appear on your tax bill.
- The assessment is multiplied by the County equalization factor to arrive at the equalized assessed value of your property or the EAV. This is also known as the taxable property value.
- The EAV is multiplied by the local tax rate to determine the gross tax due.
- If you are a homeowner, you may be entitled to receive exemptions.
- Exemptions are then deducted from the gross tax to arrive at the net tax due.